 链表的高级操作:链表的反转、合并、拆分
链表的高级操作:链表的反转、合并、拆分
# 链表的高级操作:链表的反转、合并、拆分
# 一、链表的反转
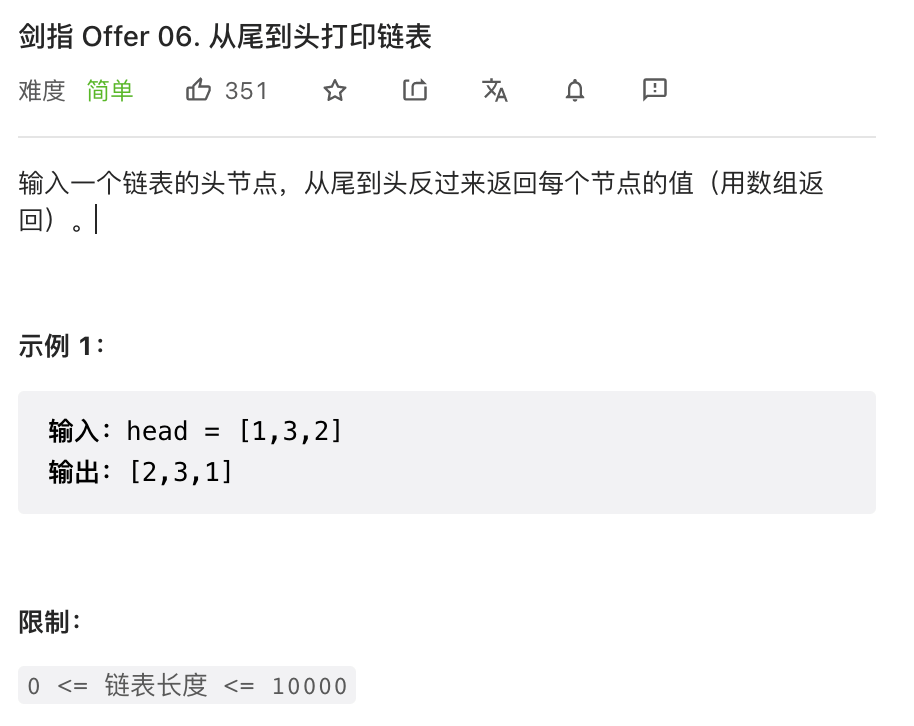
# 剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表 (opens new window)
☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️题解一:栈
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
Stack<Integer> res = new Stack<>();
while(head != null){
res.push(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int[] arr = new int[res.size()];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i] = res.pop();
}
return arr;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表 (opens new window)

☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️题解一:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null,cur = head;
while(cur != null){
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;//pre是从‘null’到‘1->null‘到’2->1>null‘的过程
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️题解二:递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//定义出口
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode current = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return current;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
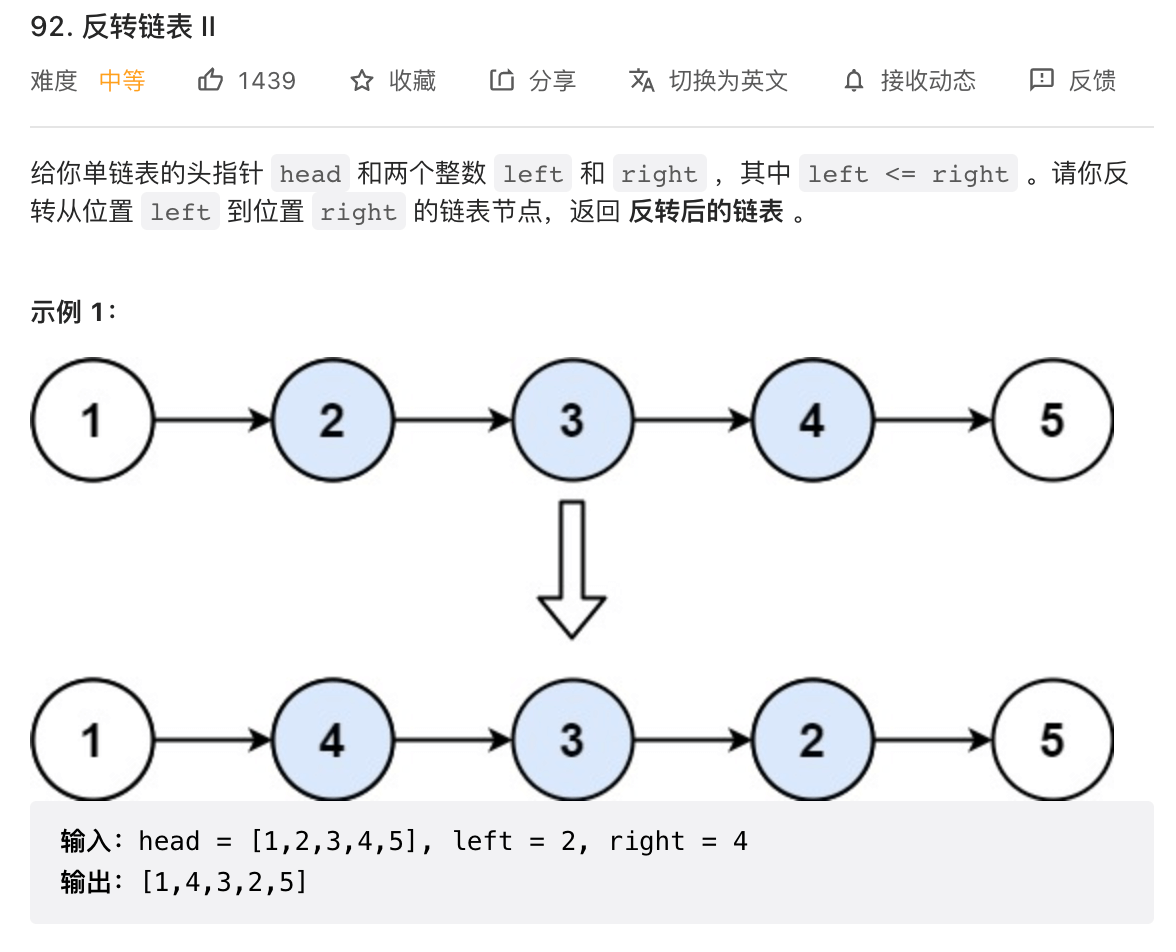
# 92. 反转链表 II (opens new window)
☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️题解一:过于无趣,只写了一段核心代码
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
//Step1: 找到left-1的位置
//Step2: 找到right+1的位置
//Step3 :反转[left,right)区间
//Step4: left-1指向刚刚反转的结果
}
//反转区间[a,b)之间的链表
public ListNode reverseNode(ListNode nodeA,ListNode nodeB){
ListNode pre = null,cur = nodeA;
while(cur != nodeB){
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️题解二:头插法
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
//Step1: 定义一个虚拟节点存放结果
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1,head);
//Step2: 初始化指针g和p,并分别指向left-1和left
ListNode g = dummy,p = dummy.next;
for(int i=0;i<left-1;i++){
g = g.next;
p = p.next;
}
//Step3: 头插法将p之后的节点插入前面
for(int i=0;i<right-left;i++){
ListNode tmp = p.next;
p.next = p.next.next;
tmp.next = g.next;
g.next = tmp;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
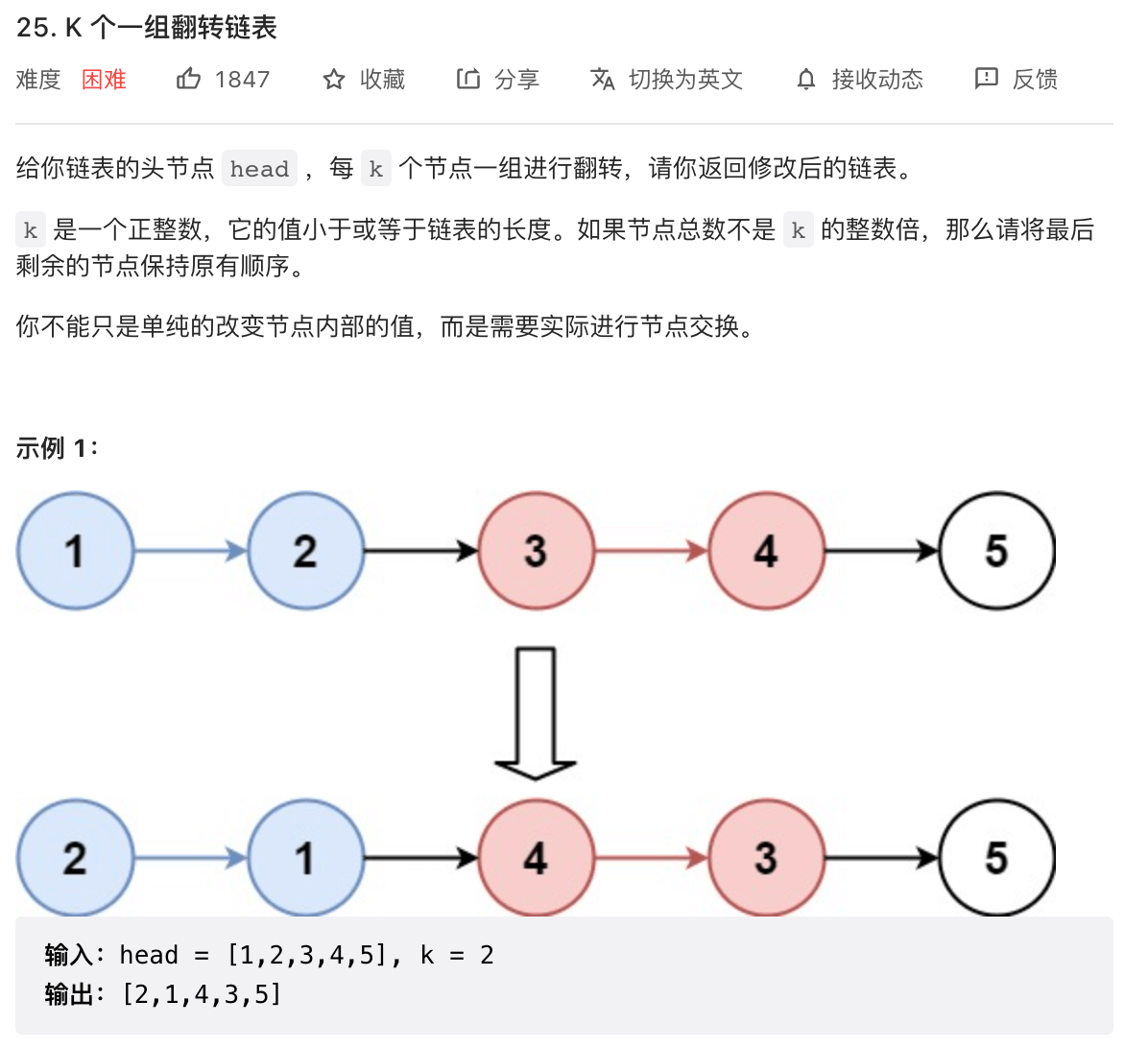
# 25. K 个一组翻转链表 (opens new window)
☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️题解一:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head == null) return null;
//Step1: 计算距离
ListNode a = head,b = head;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
if(b == null) return a;
b = b.next;
}
//Step2: 反转第一个[a,b)距离
ListNode res = reverseKTop(a,b);
//Step3: 反转子问题[b,~)距离
a.next = reverseKGroup(b,k);
return res;
}
//区间【a,b)反转
public ListNode reverseKTop(ListNode nodeA,ListNode nodeB){
ListNode pre = null,cur = nodeA;
while(cur != nodeB){
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 二、链表的合并
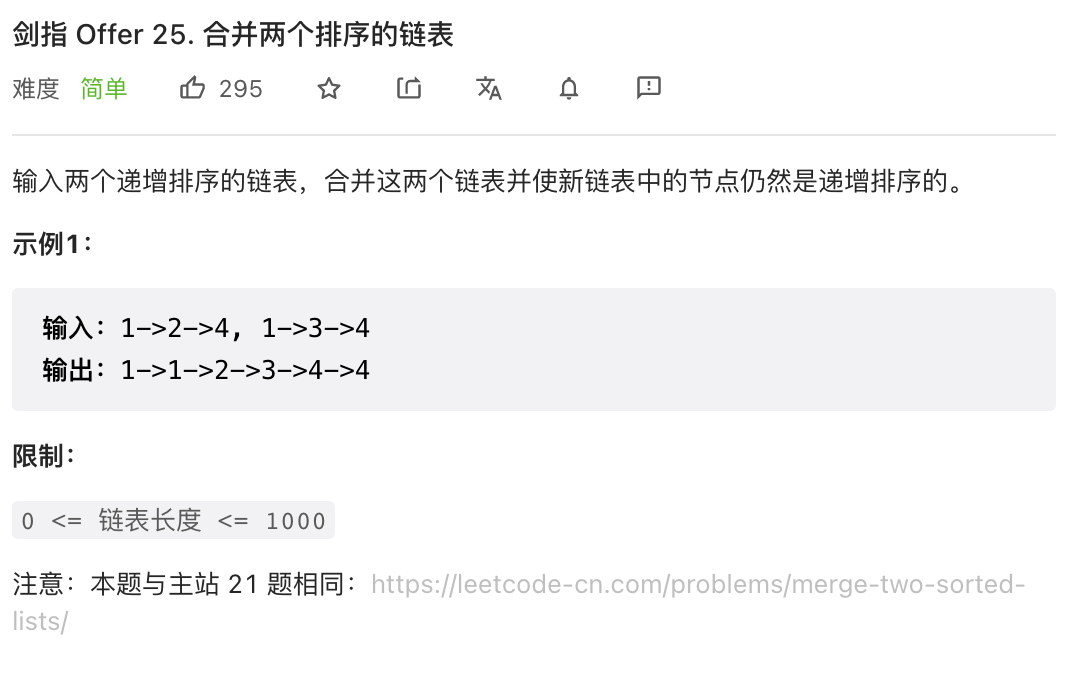
# 剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表 (opens new window)
☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️题解一:
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val < l2.val){
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = (l2 == null?l1:l2);
return dummy.next;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 剑指 Offer II 078. 合并排序链表 (opens new window)

☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️题解一:
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
//Step1: 构建优先级队列
Queue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((x,y)->x.val-y.val);
//Step2: 数据存入优先级队列
for (ListNode node : lists) {
if(node != null) queue.offer(node);
}
//Step3: 遍历队列
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode cur = dummy;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
//获取最小结果
ListNode tmp = queue.poll();
cur.next = tmp;
if(tmp.next != null){
//放入队列
queue.offer(tmp.next);
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 三、链表的拆分
# 86. 分隔链表 (opens new window)
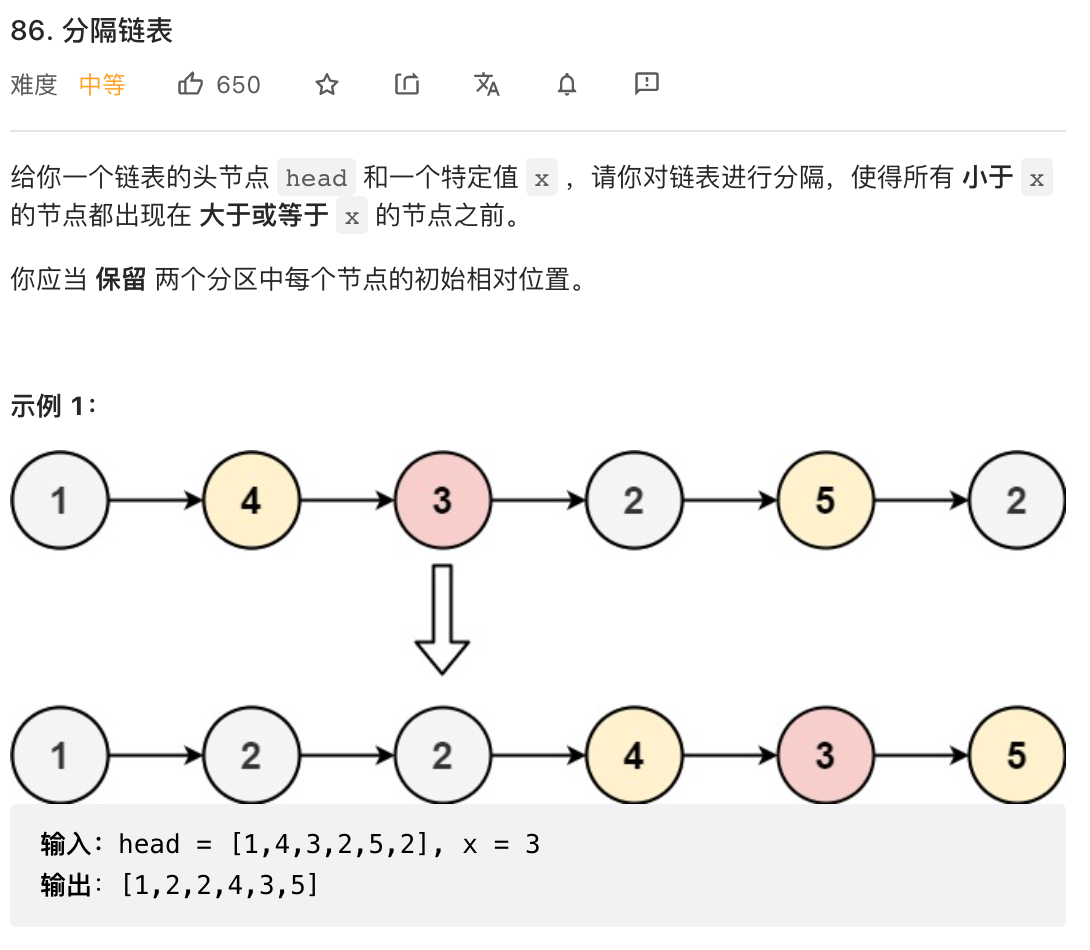
☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️☀️题解一:
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode dummyLeft = new ListNode(),dummyRight = new ListNode();
ListNode left = dummyLeft,right = dummyRight;
while(head != null){
if(head.val < x){
left.next = head;
left = left.next;
}else{
right.next = head;
right = right.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
right.next = null;//断开右边节点
left.next = dummyRight.next;
return dummyLeft.next;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
