Spring事件监听机制
Spring事件监听机制
# Spring事件监听机制
# 一、基本介绍
Spring的事件是基于观察者设计模式,包括三个组件:事件,事件监听器,事件广播器
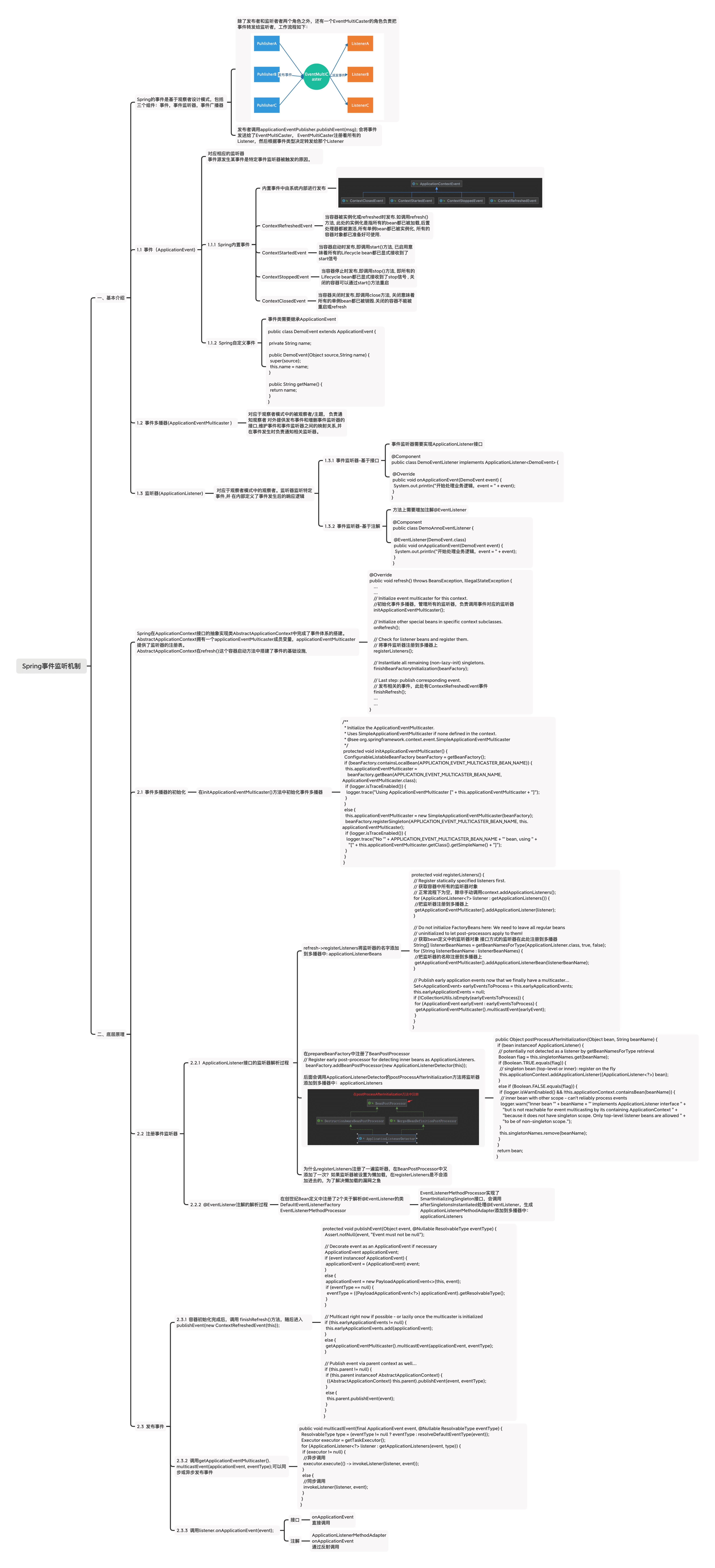
除了发布者和监听者者两个角色之外,还有一个EventMultiCaster的角色负责把事件转发给监听者,工作流程如下:
发布者调用applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(msg) 会将事件发送给EventMultiCaster, EventMultiCaster注册着所有的Listener,然后根据事件类型决定转发给那个Listener
# 1.1 事件(ApplicationEvent)
对应相应的监听器 。事件源发生某事件是特定事件监听器被触发的原因。
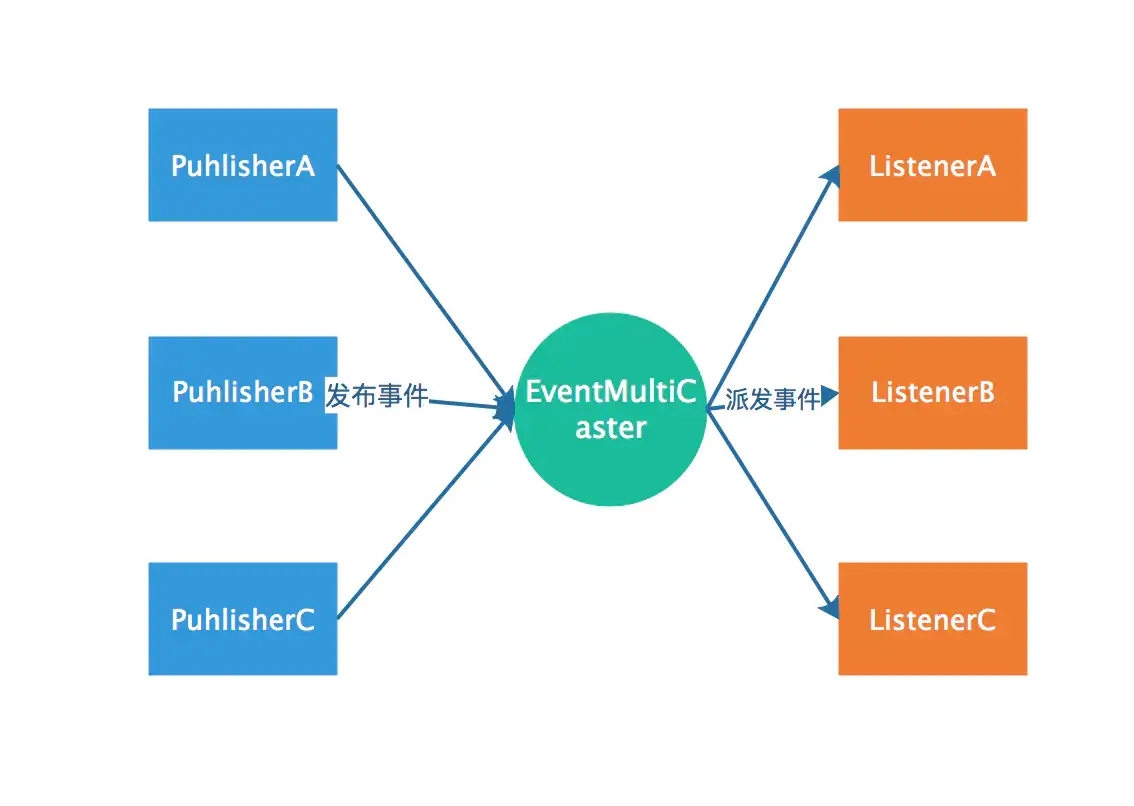
# 1.1.1 Spring内置事件
内置事件中由系统内部进行发布
ContextRefreshedEvent当容器被实例化或refreshed时发布.如调用refresh()方法, 此处的实例化是指所有的bean都已被加载,后置处理器都被激活,所有单例bean都已被实例化, 所有的容器对象都已准备好可使用.ContextStartedEvent当容器启动时发布,即调用start()方法, 已启用意味着所有的Lifecycle bean都已显式接收到了start信号ContextStoppedEvent当容器停止时发布,即调用stop()方法, 即所有的Lifecycle bean都已显式接收到了stop信号 , 关闭的容器可以通过start()方法重启ContextClosedEvent当容器关闭时发布,即调用close方法, 关闭意味着所有的单例bean都已被销毁.关闭的容器不能被重启或refresh
# 1.1.2 Spring自定义事件
事件类需要继承ApplicationEvent
public class DemoEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String name;
public DemoEvent(Object source,String name) {
super(source);
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 1.2 事件多播器(ApplicationEventMulticaster )
对应于观察者模式中的被观察者/主题 。负责通知观察者对外提供发布事件和增删事件监听器的接口,维护事件和事件监听器之间的映射关系,并在事件发生时负责通知相关监听器。
# 1.3 监听器(ApplicationListener)
对应于观察者模式中的观察者。监听器监听特定事件,并在内部定义了事件发生后的响应逻辑
# 1.3.1 事件监听器-基于接口
事件监听器需要实现ApplicationListener接口
@Component
public class DemoEventListener implements ApplicationListener<DemoEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(DemoEvent event) {
System.out.println("开始处理业务逻辑,event = " + event);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 1.3.2 事件监听器-基于注解
方法上需要增加注解@EventListener
@Component
public class DemoAnnoEventListener {
@EventListener(DemoEvent.class)
public void onApplicationEvent(DemoEvent event) {
System.out.println("开始处理业务逻辑,event = " + event);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 二、底层原理
Spring在ApplicationContext接口的抽象实现类AbstractApplicationContext中完成了事件体系的搭建。
AbstractApplicationContext拥有一个applicationEventMulticaster成员变量,applicationEventMulticaster提供了监听器的注册表。
AbstractApplicationContext在refresh()这个容器启动方法中搭建了事件的基础设施,
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
...
...
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
//初始化事件多播器,管理所有的监听器,负责调用事件对应的监听器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 将事件监听器注册到多播器上
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 发布相关的事件,此处有ContextRefreshedEvent事件
finishRefresh();
...
...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 2.1 事件多播器的初始化
在initApplicationEventMulticaster()方法中初始化事件多播器
/**
* Initialize the ApplicationEventMulticaster.
* Uses SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster if none defined in the context.
* @see org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
*/
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 2.2 注册事件监听器
# 2.2.1 ApplicationListener接口的监听器解析过程
refresh()->registerListeners()将监听器的名字添加到多播器中:applicationListenerBeansprotected void registerListeners() { // Register statically specified listeners first. // 获取容器中所有的监听器对象 // 正常流程下为空,除非手动调用context.addApplicationListeners(); for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) { //把监听器注册到多播器上 getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them! // 获取bean定义中的监听器对象 接口方式的监听器在此处注册到多播器 String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false); for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) { //把监听器的名称注册到多播器上 getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName); } // Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster... Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents; this.earlyApplicationEvents = null; if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) { for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27在
prepareBeanFactory()中注册了BeanPostProcessor// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners. beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));1
2
后面会调用ApplicationListenerDetector的postProcessAfterInitialization方法将监听器添加到多播器中:applicationListeners
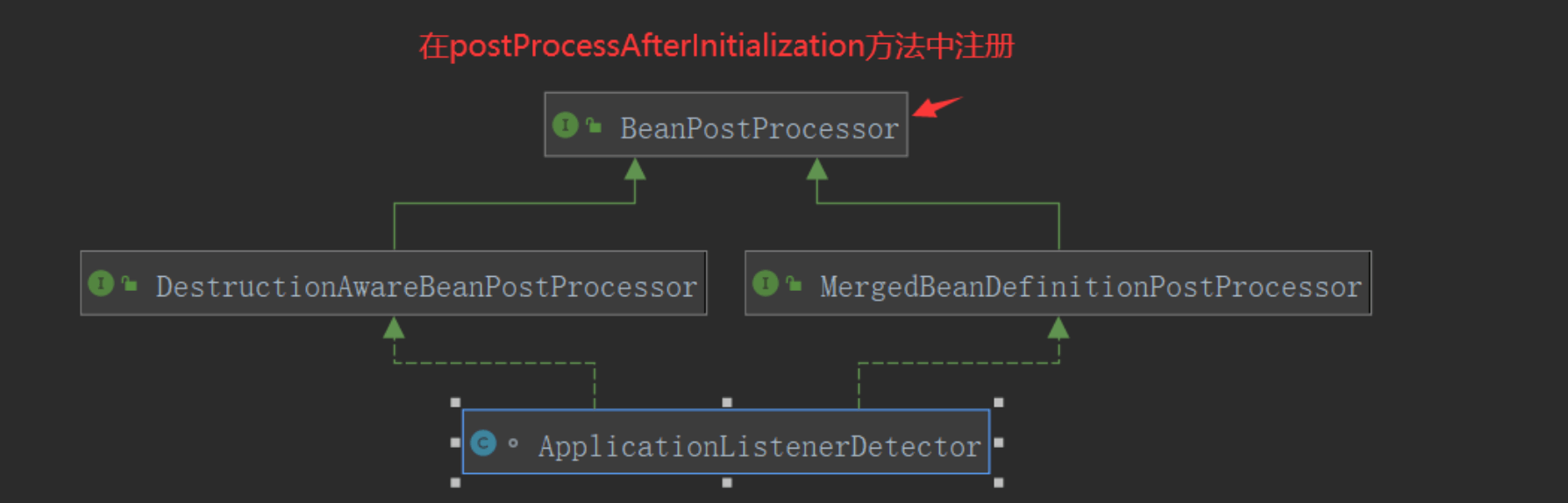
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationListener) {
// potentially not detected as a listener by getBeanNamesForType retrieval
Boolean flag = this.singletonNames.get(beanName);
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(flag)) {
// singleton bean (top-level or inner): register on the fly
this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean);
}
else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(flag)) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && !this.applicationContext.containsBean(beanName)) {
// inner bean with other scope - can't reliably process events
logger.warn("Inner bean '" + beanName + "' implements ApplicationListener interface " +
"but is not reachable for event multicasting by its containing ApplicationContext " +
"because it does not have singleton scope. Only top-level listener beans are allowed " +
"to be of non-singleton scope.");
}
this.singletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
}
return bean;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
为什么
registerListeners注册了一遍监听器,在BeanPostProcessor中又添加了一次?如果监听器被设置为懒加载,在
registerListeners是不会添加进去的,为了解决懒加载的漏网之鱼
# 2.2.2 @EventListener注解的解析过程
在创世纪Bean定义中注册了2个关于解析@EventListener的类
DefaultEventListenerFactory和EventListenerMethodProcessor
其中EventListenerMethodProcessor实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口,会调用afterSingletonsInstantiated处理@EventListener,生成ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter添加到多播器中:applicationListeners
# 2.3 发布事件
# 2.3.1 容器初始化完成后,调用 finishRefresh()方法,随后进入publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this))
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# 2.3.2 调用getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType)可以同步或异步发布事件
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
//异步调用
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
//同步调用
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 2.3.3 调用listener.onApplicationEvent(event)
- 接口方式
onApplicationEvent直接调用 - 注解方式
ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter.onApplicationEvent通过反射调用
# 三、思维导图